MS Project Writeup
06 May 2024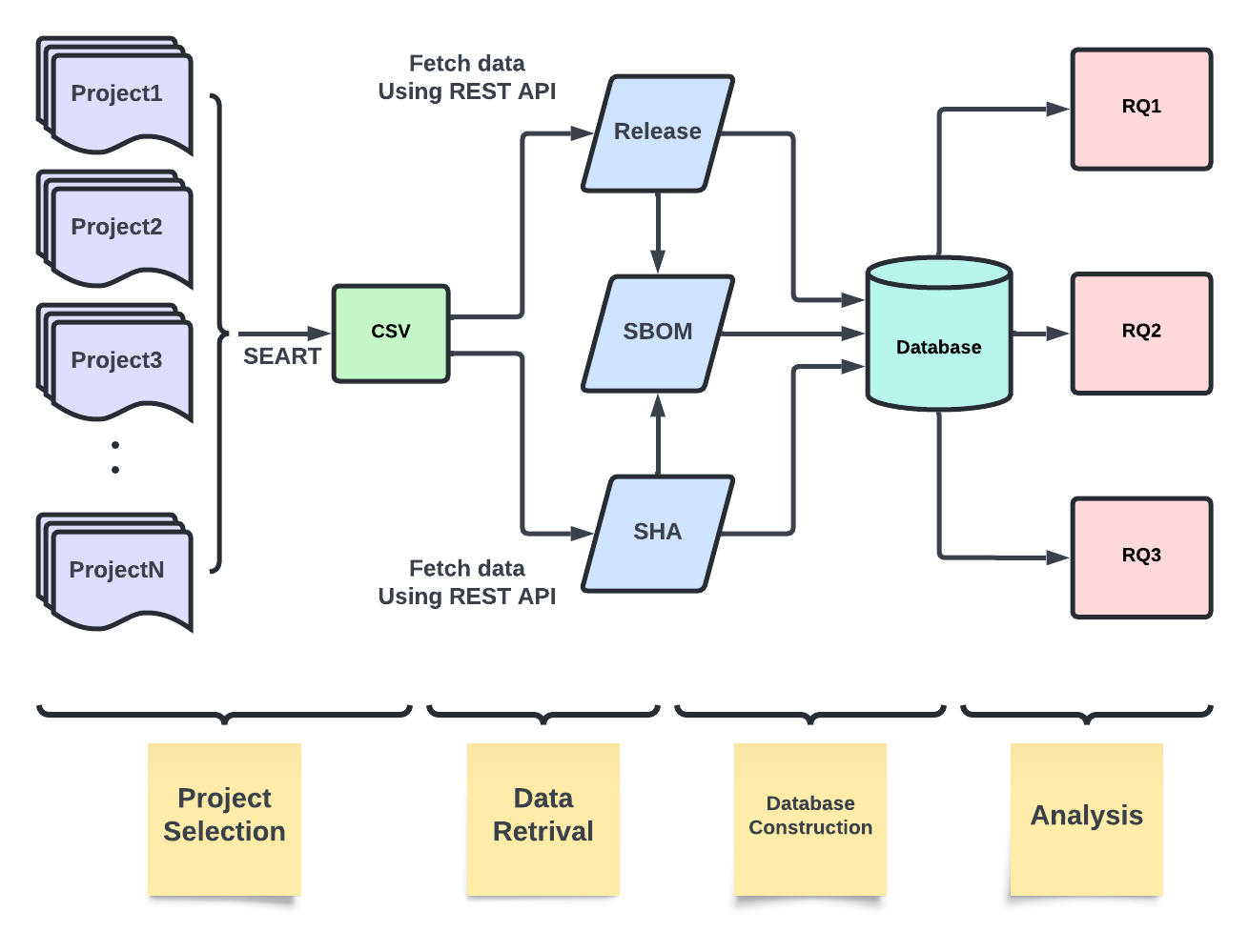
Introduction
In today’s software-centric landscape, comprehending the intricate interplay of dependencies within a project stands as a pivotal pillar for ensuring security, compliance, and transparency. As software ecosystems burgeon in complexity, the imperative for robust documentation of these dependencies has never been more pronounced. This is precisely where the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) assumes its significance.
Originating from the manufacturing industry, where a bill of materials (BOM) served as an inventory roster of sub-assemblies and components within a parent assembly, the SBOM emerges as the software equivalent—a foundational construct vital for fortifying software supply chain security. Functioning as a nested inventory, the SBOM meticulously enumerates the software components comprising a project. It delineates these components, furnishing pertinent information and delineating the supply chain relationships interlinking them. Essentially, the SBOM functions as a comprehensive ledger, cataloging all components, libraries, frameworks, and software artifacts incorporated within a project. Its utility lies in furnishing invaluable insights into the project’s composition, empowering developers, stakeholders, and security professionals to navigate vulnerability management, licensing compliance, and risk mitigation strategies with informed precision. However, despite the manifold benefits of SBOMs, their adoption trajectory remains somewhat subdued. A significant proportion of existing third-party software or components—whether open source or proprietary—lack accompanying SBOMs. Ideally, SBOM generation should commence early in the software development life cycle, gradually accruing enriched information through subsequent stages. The absence of a unified package manager exacerbates this issue in the realm of C/C++ development, rendering SBOM generation an arduous task. Nonetheless, during our preliminary investigations, we discerned that GitHub’s built-in SBOM feature seemed poised to provide insights into C/C++ projects, prompting us to delve deeper into its potential.
This document serves as an instructional blueprint for conducting an SBOM study on C/C++ projects hosted on GitHub. Through meticulous analysis, extraction, and documentation of dependencies and associated metadata, our objective is to address the following research questions (RQs):
- RQ1: How frequently do developers update project dependencies?
Understanding the cadence of updates to project dependencies is pivotal for gauging project maintenance and evolution. Through scrutiny of version control history, commit logs, and release notes, we endeavor to discern the frequency with which developers integrate dependency updates. Factors such as the project’s development tempo, the exigency of security patches, and the availability of new features or bug fixes in upstream dependencies influence update frequency. Furthermore, examining patterns of dependency updates over time offers insights into the project’s overarching maintenance strategy and its responsiveness to emergent issues and advancements within the software realm.
- RQ2: What are the common libraries that undergo changes?
Unveiling common libraries subject to changes provides valuable insights into evolving project requisites, technological trends, and community-driven development dynamics. By parsing through version control history and dependency manifests, we aim to pinpoint libraries frequently updated or replaced. These may encompass core dependencies like frameworks, utility libraries, or platform-specific components. Understanding the rationale behind these changes can illuminate the project’s adaptability to evolving technologies, performance enhancements, or shifts in development paradigms.
- RQ3: What are the reasons behind these changes?
Delving into the motives driving dependency changes furnishes contextual understanding of the project’s development trajectory and decision-making ethos. By dissecting the rationale underlying dependency alterations, we aspire to glean deeper insights into the project’s prioritization of stability, security, performance, and feature enhancements. Furthermore, this exploration sheds light on the project’s alignment with industry standards and best practices, elucidating its strategic evolution within the software landscape.
Methodology
The methodology employed for establishing the database aimed to ensure systematic organization and comprehensive coverage of Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) information extracted from GitHub repositories. Through meticulous project selection criteria, data retrieval procedures, and database construction steps as shown in Figure above, we laid the foundation for a robust dataset conducive to in-depth analysis and inquiry.
Conclusion
The findings from this study shed light on various aspects of dependency management practices and their implications for software development. Through the exploration of three research questions, we gained insights into the frequency of dependency updates, common libraries undergoing changes, and the reasons behind dependency changes.
Firstly, our analysis of the frequency of dependency updates revealed a wide spectrum of update patterns across software projects. While some projects exhibit minimal changes and stable release intervals, others demonstrate dynamic update cycles with frequent releases. Understanding these patterns is crucial for developers to optimize resource allocation, balance stability with innovation, and ensure the overall health of software projects.
Secondly, our investigation into common libraries undergoing changes highlighted the prevalence of GitHub Actions workflows and diverse ecosystems of dependencies. GitHub Actions workflows play a pivotal role in enabling automation and CI/CD processes, while the heterogeneous nature of dependency ecosystems underscores the diversity of tools and technologies used in software development.
Finally, our examination of the reasons behind dependency changes uncovered common themes and patterns in release notes and commit messages. By analyzing textual data, we identified prevalent terms and phrases indicative of bug fixes, feature enhancements, and performance optimizations. Understanding these reasons can inform developers’ decisions regarding prioritization, resource allocation, and overall software quality improvement efforts.
In conclusion, this study provides valuable insights into dependency management practices and their implications for software development. By leveraging these insights, developers can make informed decisions to optimize their development workflows, ensure project stability, and deliver high-quality software products to end-users.